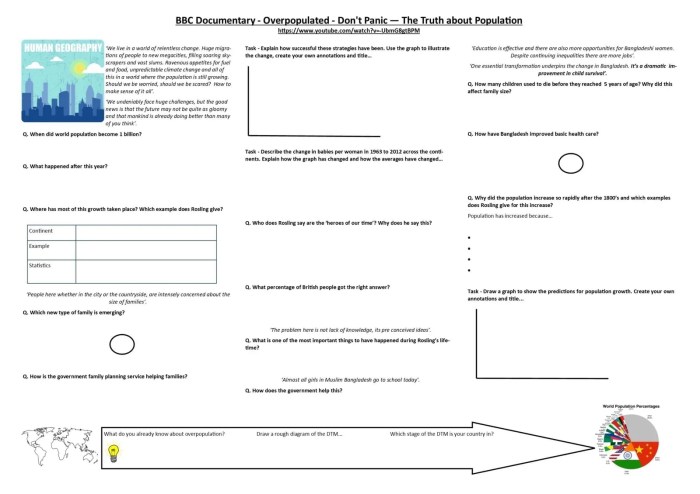
Don’t panic the truth about population worksheet answers – Embark on a journey with “Don’t Panic: The Truth About Population Worksheet Answers,” a thought-provoking guide that unravels the complexities of population dynamics. This comprehensive resource delves into the theories, trends, and consequences of population growth, equipping you with a deeper understanding of one of humanity’s most pressing challenges.
From the Malthusian theory to the demographic transition model, we explore the historical and contemporary perspectives on population growth. We examine the factors driving population change, including birth rates, mortality rates, and migration patterns. The environmental implications of population growth are also brought to light, highlighting the urgent need for sustainable solutions.
Population Growth
Population growth refers to the increase in the number of individuals in a population over time. It can be measured as the change in population size over a specific period, usually expressed as a percentage.
Factors Contributing to Population Growth
- Birth rate: The number of births per 1,000 people in a population.
- Death rate: The number of deaths per 1,000 people in a population.
- Net migration: The difference between the number of people entering and leaving a population.
Examples of Rapid Population Growth
Several countries and regions have experienced rapid population growth in recent decades, including:
- India
- China
- Sub-Saharan Africa
The Malthusian Theory
Thomas Malthus, an English economist, proposed a theory of population growth in the late 18th century. Malthus believed that population growth would inevitably lead to scarcity and poverty because the human population would grow faster than the food supply.
Key Principles of Malthus’s Theory
- Population growth is exponential, while food production grows linearly.
- The human population will inevitably outgrow its food supply, leading to famine and disease.
- War, famine, and disease are natural checks on population growth.
Criticisms of Malthus’s Theory
Malthus’s theory has been criticized on several grounds, including:
- Technological advancements can increase food production faster than population growth.
- Population growth can slow down as countries undergo economic development.
- Government policies can influence population growth rates.
The Demographic Transition Model: Don’t Panic The Truth About Population Worksheet Answers
The demographic transition model is a framework that describes the stages of population change that countries typically undergo as they develop. The model has four stages:
Stages of the Demographic Transition Model
- Pre-industrial stage:High birth and death rates, resulting in slow population growth.
- Transitional stage:Birth rates remain high, but death rates decline, leading to rapid population growth.
- Industrial stage:Birth rates decline as countries develop economically, leading to slower population growth.
- Post-industrial stage:Both birth and death rates are low, resulting in stable or declining population growth.
Limitations of the Demographic Transition Model
The demographic transition model is a useful framework for understanding population change, but it has some limitations:
- It does not apply to all countries.
- It does not account for factors such as migration and urbanization.
- It does not predict the timing or pace of population change.
Population Control Measures
Population control measures are policies and programs designed to reduce or stabilize population growth. These measures have been used throughout history and include:
Methods of Population Control
- Family planning programs
- Education and empowerment of women
- Economic incentives and disincentives
- Coercion and forced sterilization
Ethical Implications of Population Control, Don’t panic the truth about population worksheet answers
Population control measures can raise ethical concerns, including:
- 侵犯个人自由
- Diskriminasi terhadap kelompok tertentu
- Dampak negatif pada kesehatan dan kesejahteraan
Examples of Successful Population Control Policies
Several countries have implemented successful population control policies, including:
- China’s one-child policy
- India’s family planning program
- Bangladesh’s microcredit program
The Impact of Population Growth on the Environment
Rapid population growth can have a significant impact on the environment, including:
Environmental Challenges Associated with Population Growth
- Increased resource consumption
- Deforestation and habitat loss
- Pollution and climate change
- Water scarcity
Examples of Environmental Problems Caused by Population Growth
Population growth has contributed to environmental problems in various parts of the world, including:
- Deforestation in the Amazon rainforest
- Water shortages in the Middle East
- Air pollution in major cities
The Future of Population Growth
The future of population growth is uncertain, but several factors will likely influence future trends:
Factors Influencing Future Population Growth
- Economic development
- Education and empowerment of women
- Government policies
- Technological advancements
Potential Consequences of Different Population Growth Scenarios
Different population growth scenarios could have significant consequences, including:
- High population growth:Increased environmental degradation, resource shortages, and social instability.
- Low population growth:Aging population, economic slowdown, and labor shortages.
- Stable population growth:Sustainable resource use, balanced economic growth, and social stability.
FAQ
What is exponential population growth?
Exponential population growth occurs when the population size increases at a constant percentage rate, leading to a rapid and unsustainable increase in population size.
What are the key principles of Malthus’s population theory?
Malthus’s theory states that population growth is limited by resources, leading to a struggle for survival and the prevention of population growth beyond the carrying capacity of the environment.
What are the stages of the demographic transition model?
The demographic transition model describes four stages of population change: pre-industrial, transitional, industrial, and post-industrial, each characterized by different patterns of birth and death rates.