Embark on a captivating journey through the ancient cartographic world of China with our comprehensive ancient china map answer key. Dive into the depths of history, uncovering the evolution of these maps and their profound impact on shaping Chinese civilization.
From the earliest silk scrolls to intricate paper masterpieces, ancient China maps played a pivotal role in navigation, administration, and military strategy. They not only charted the physical landscape but also reflected the cultural and philosophical beliefs of their time.
Ancient China Maps
Ancient China maps hold significant historical value, showcasing the cartographic advancements and geographical understanding of ancient Chinese civilizations. These maps evolved over time, reflecting the changing political landscape, technological innovations, and cultural influences.
Early Maps, Ancient china map answer key
The earliest known maps of China date back to the Warring States period (475-221 BCE). These maps were often drawn on silk or bamboo and depicted the major rivers, mountains, and cities of the time. One notable example is the “Yu Gong” map, which was included in the Book of Documents and provided a detailed description of the geography of China.
Later Maps
During the Han Dynasty (206 BCE-220 CE), Chinese cartography flourished. The most famous map from this period is the “Map of the Silk Road,” which was created by Zhang Heng in 125 CE. This map depicted the extensive network of trade routes that connected China with Central Asia and Europe.
Purposes of Ancient China Maps
Ancient China maps served various purposes, including:
- Navigation:Maps were used by travelers and merchants to plan their journeys and navigate the vast landscapes of China.
- Administration:Maps were used by government officials to manage territories, collect taxes, and plan military campaigns.
- Military Strategy:Maps were essential for military commanders to plan battles and anticipate the movements of enemy forces.
Cartographic Techniques in Ancient China
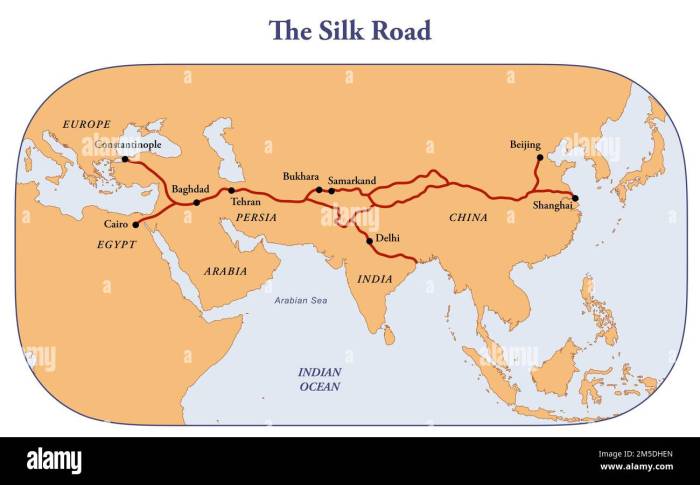
The ancient Chinese developed sophisticated cartographic techniques that evolved over centuries. They used various materials, scales, projections, and symbols to create maps that served practical and symbolic purposes.
Materials and Methods
- Silk:Early Chinese maps were drawn on silk, a durable and lightweight material that allowed for intricate details.
- Paper:As papermaking technology advanced, it became the preferred material for maps due to its availability and affordability.
- Engraving:Maps were also engraved on stone or metal plates, which enabled mass production and greater accuracy.
Scales and Projections
Chinese maps employed various scales, ranging from large-scale regional maps to small-scale world maps. Projections varied, including rectangular, trapezoidal, and cylindrical projections. The choice of projection depended on the intended purpose and the region being mapped.
Symbolism and Conventions
Chinese maps incorporated rich symbolism and conventions. Colors had specific meanings, with red representing south, black representing north, and yellow representing the center. Shapes and orientations also carried symbolic significance. For example, mountains were often depicted as triangles, and rivers as blue lines.
The orientation of maps varied, with some oriented towards the north and others towards the south.
Geographical Features Depicted on Ancient China Maps
Ancient China maps provide valuable insights into the geographical knowledge and cartographic techniques of ancient Chinese civilizations. These maps depict various geographical features, including mountains, rivers, and cities, which held significant cultural and historical importance.
Mountains
Mountains played a crucial role in ancient Chinese culture, often associated with sacredness and spirituality. Major mountain ranges depicted on ancient maps include the Kunlun Mountains, believed to be the abode of immortals, and the Taihang Mountains, forming a natural boundary between North and South China.
Rivers
Rivers were essential for transportation, irrigation, and settlement. The Yellow River (Huang He) and Yangtze River (Chang Jiang), two of the longest rivers in the world, are prominently featured on ancient maps. These rivers served as major arteries of commerce and cultural exchange.
The ancient Chinese maps are fascinating artifacts that provide a glimpse into the past. The intricate details and elaborate symbolism offer insights into the culture and beliefs of the time. If you’re looking for an in-depth analysis of these maps, consider reading Naomi Klein’s “Let Them Drown.”
Klein’s work explores the broader themes of climate change and environmental justice, connecting the ancient maps to contemporary issues. Returning to the ancient China map answer key, it’s clear that these maps remain a valuable resource for understanding the past and present.
Cities
Ancient China maps also show the locations of important cities, such as the capital Chang’an (modern Xi’an) and the port city of Guangzhou. These cities were centers of political, economic, and cultural activity, connecting China with the rest of the world through trade routes.
Accuracy and Completeness
Compared to modern maps, ancient China maps exhibit varying levels of accuracy and completeness. While they provide a general overview of the geographical features, the scale and precision are often limited. However, they offer valuable insights into the geographical understanding of ancient Chinese cartographers and the evolution of mapmaking techniques over time.
Cultural and Historical Context of Ancient China Maps
Ancient China maps played a significant role in shaping Chinese perceptions of their world and place within it. They provided a visual representation of the known world, which helped to define China’s borders, its relationship with neighboring countries, and its place in the broader global landscape.
Influence of Political, Economic, and Social Factors
The development of ancient China maps was heavily influenced by political, economic, and social factors. Political power struggles and territorial disputes led to the creation of maps that reflected the changing boundaries of the Chinese empire. Economic factors, such as trade and the need for resources, also influenced the development of maps, as they helped to identify and exploit new opportunities.
Connections to Chinese Art and Literature
Ancient China maps also had close connections to other forms of Chinese art and literature. They shared many of the same artistic conventions, such as the use of calligraphy and symbolism. Additionally, maps were often used to illustrate historical events and stories, providing a visual context for understanding Chinese history and culture.
FAQ Overview: Ancient China Map Answer Key
What were the earliest known ancient China maps?
The earliest known ancient China maps date back to the Warring States period (475-221 BCE) and were found on silk scrolls.
What were the main purposes of ancient China maps?
Ancient China maps were used for a variety of purposes, including navigation, administration, military strategy, and religious rituals.
What materials were used to create ancient China maps?
Ancient China maps were typically created on silk, paper, or wood, using materials such as ink, paint, and engraving.
How accurate were ancient China maps?
The accuracy of ancient China maps varied depending on the scale, projection, and techniques used. While some maps were remarkably accurate, others were more symbolic or conceptual.
What is the significance of ancient China maps in understanding Chinese history and culture?
Ancient China maps provide valuable insights into the Chinese worldview, their understanding of geography, and the development of their civilization.
